Google Earth Engine
Introduction
Google Earth Engine (GEE) is cloud-based geographic information system (GIS) that is (currently) free to use for educational and research purposes. We will be using GEE for most of the heavy lifting in this course: accessing large datasets, crunching them in computational workflows, and visualizing them with web maps. The lovely thing about GEE is that all of this work gets done on Google’s servers in the cloud. All you will need to work with GEE is a web browser, preferably Google Chrome, and a decent internet connection. All you need to do is sign up for the Google Earth Engine cloud service.
Please complete the steps below on the first day of class (or 24 hours before our first lab meeting).
Sign up for Earth Engine
-
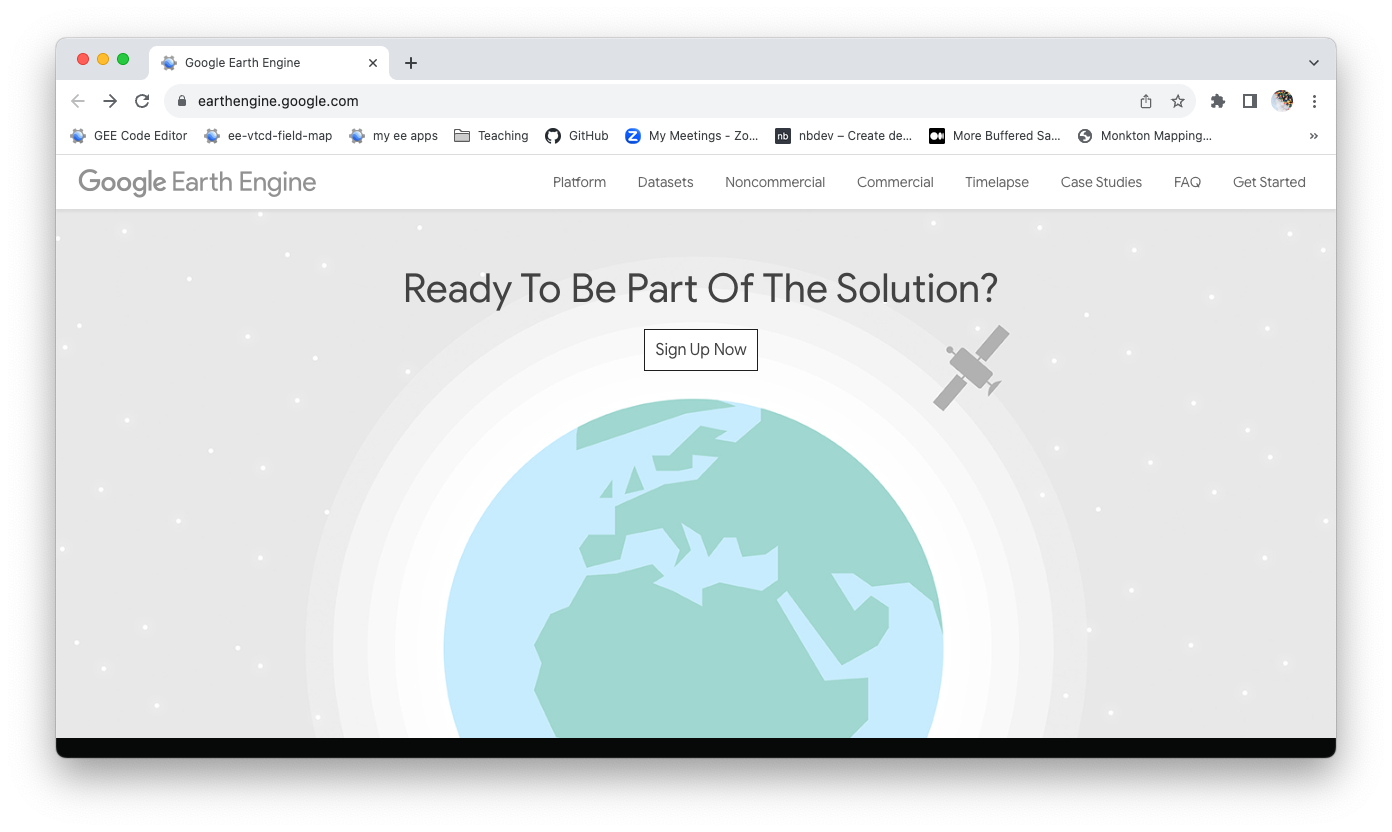
Go to the bottom of the Google Earth Engine page and click ‘Sign Up Now’.
-
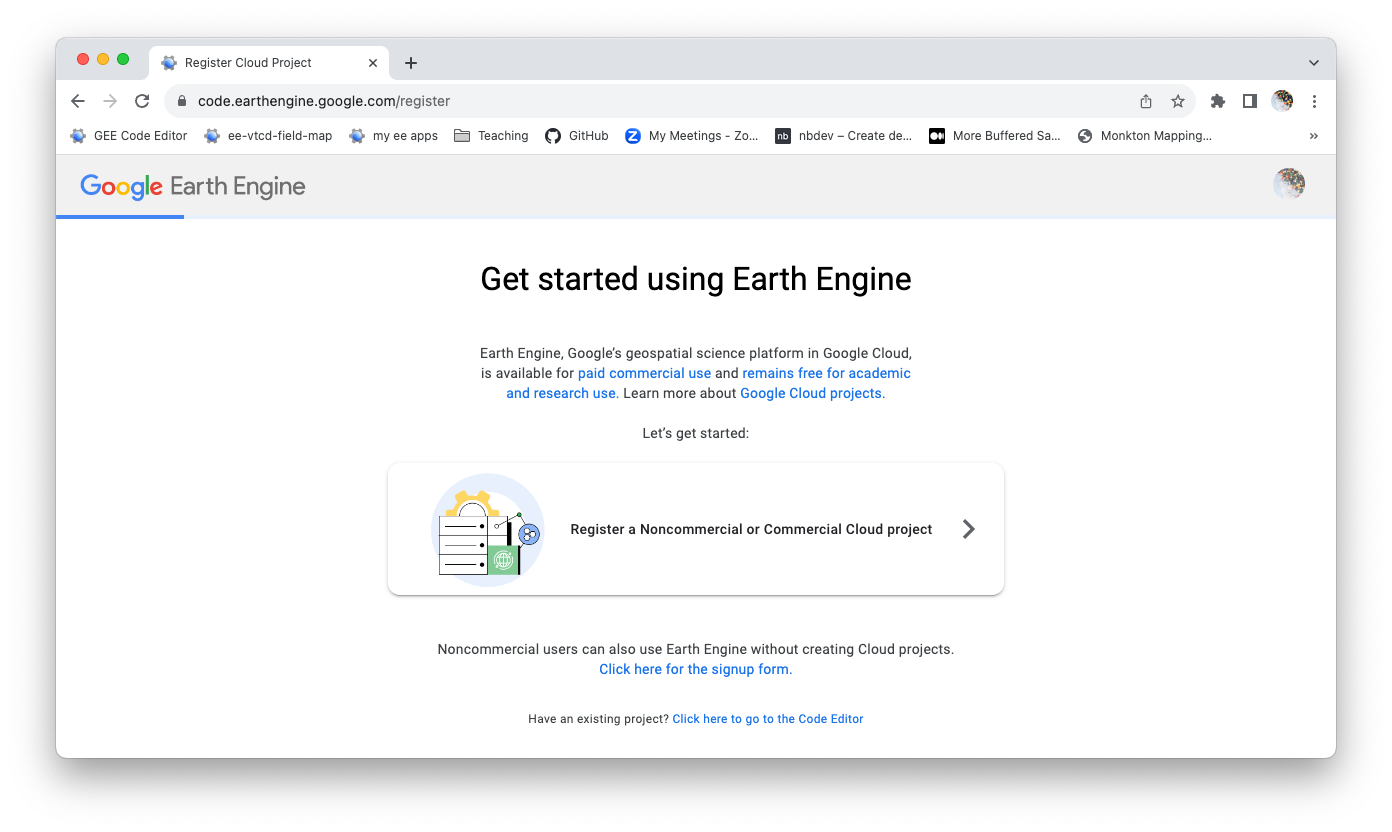
You want to sign up for a noncommercial cloud project. The next page will likely only show one option, so go ahead and click that.
-
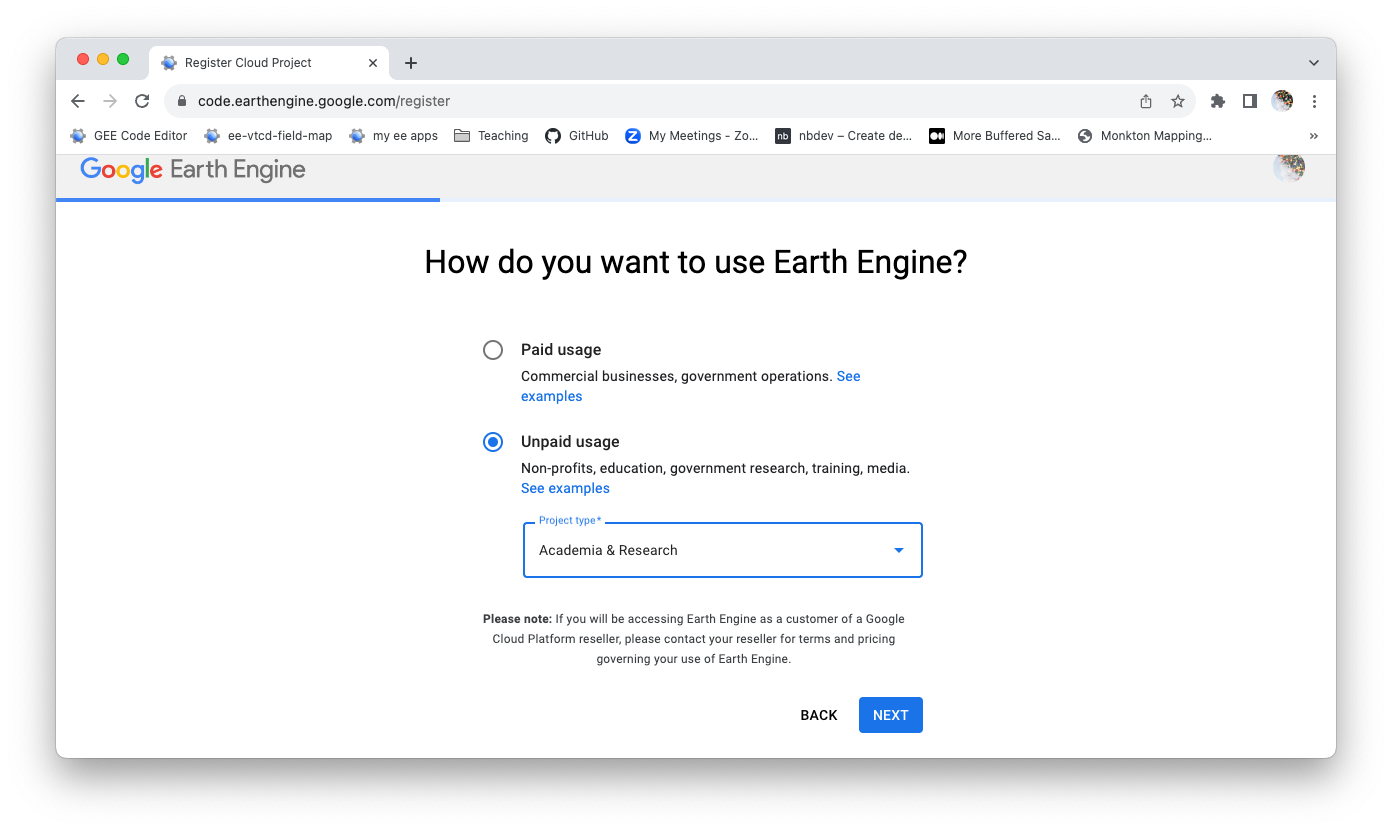
As a student, you do not have to pay for your use of Earth Engine. So click ‘Unpaid usage’ and then select ‘Academic and Research’ from the pull-down options. Click ‘Next’ to move on.
-
You should create a new Google Cloud Project. You can try doing this under the middlebury.edu organization. Your user name should be ‘ee-your-midd-email-address-name’ with no spaces. For example, ‘ee-jhowarth’. Then click ‘Continue to Summary’.
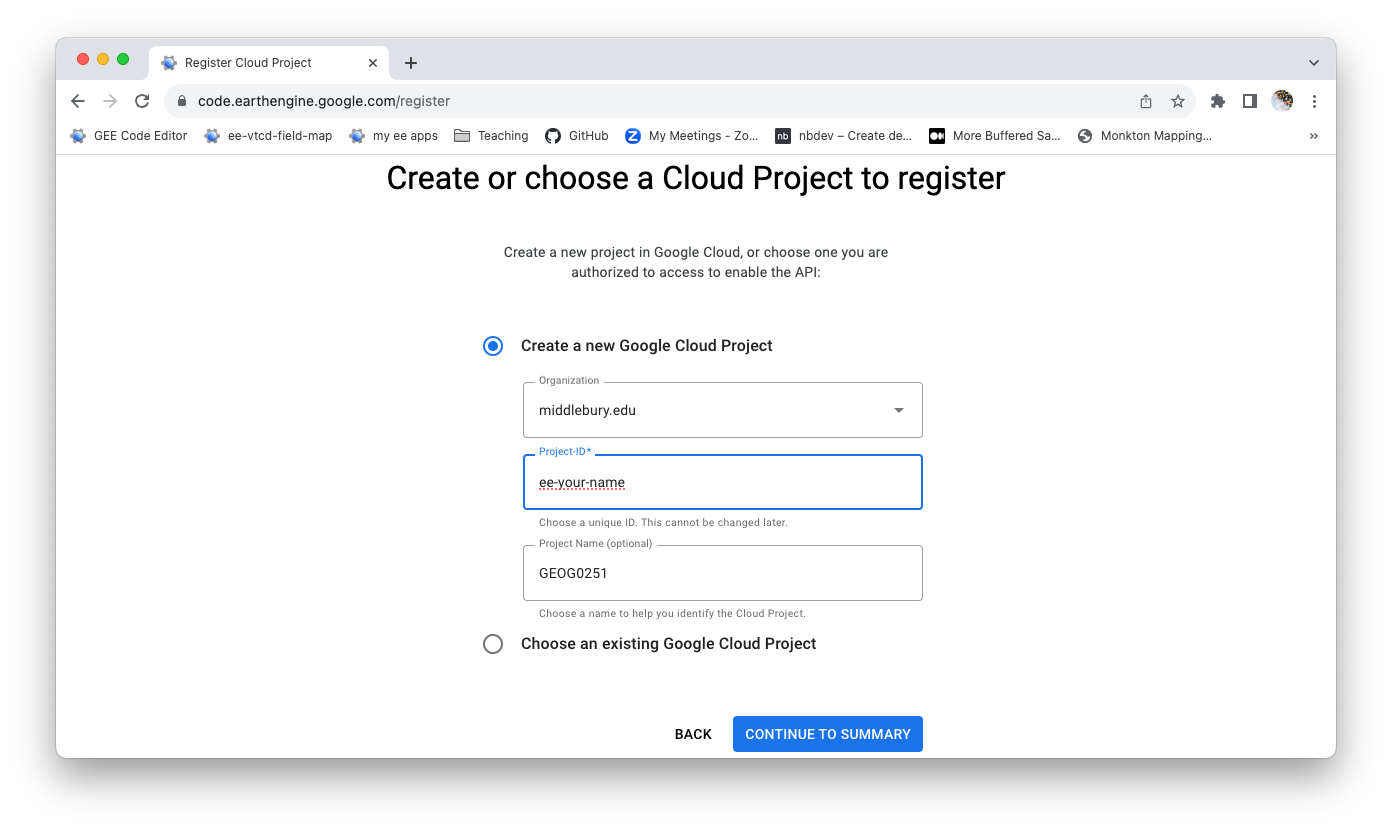
-
Affirm the summary to finalize the project.
-
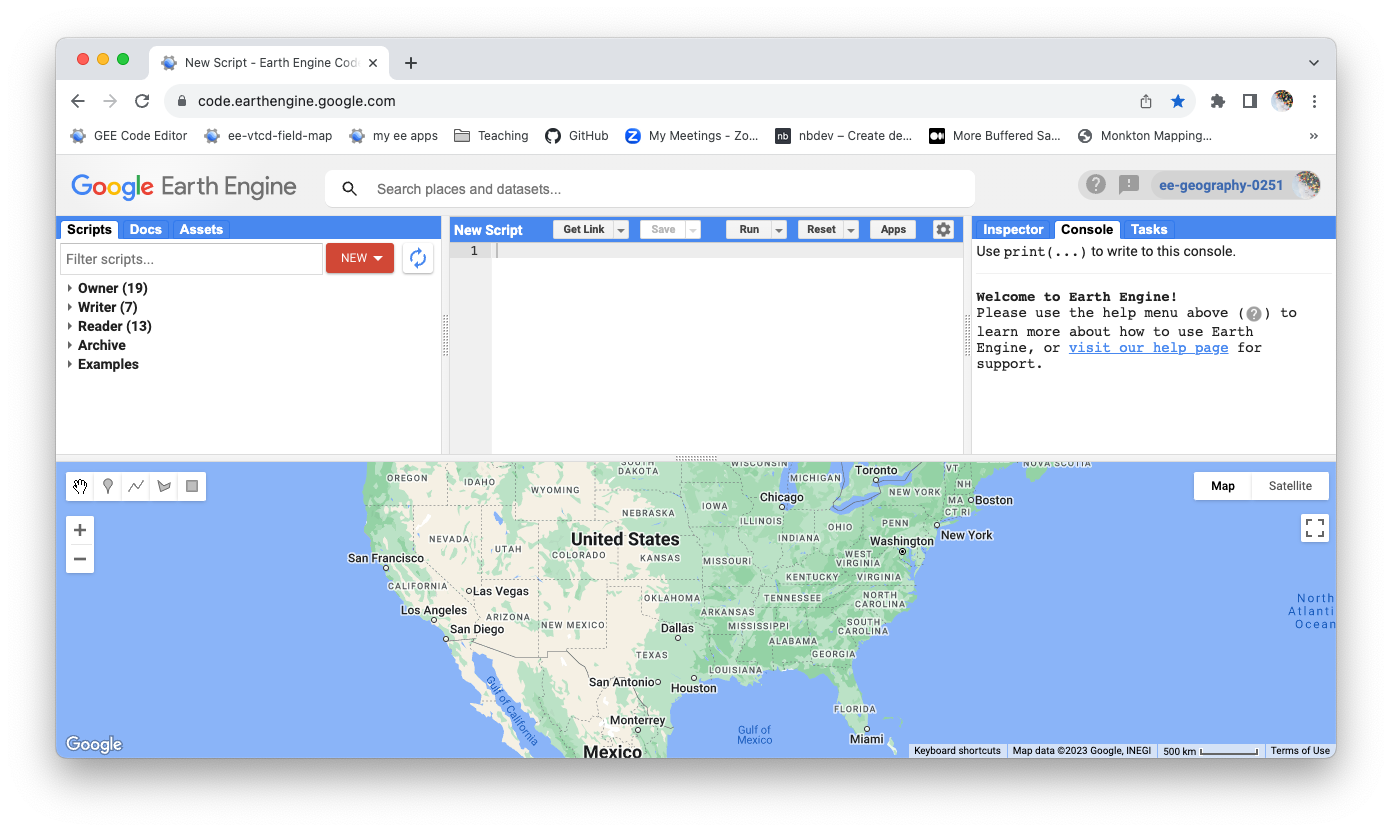
It may take a little time for you to receive approval. When you are successful, you should be able to open the Code Editor and get to a page that looks similar to the one below.